Solutions
Navigating the Compliance Landscape
Main topics today
complAIzer is based on a comprehensive customer survey, focusing on 3 central application areas

Privacy & data management
… refers to privacy compliance and the effective management of data in organizations. It includes the development, implementation and controlling of policies, procedures and technologies to protect the privacy of individuals, regulate the collection and processing of data, and ensure the security and integrity of data to meet legal requirements and compliance standards.

Supply chain management
… as a subfield of compliance deals with the adherence to legal, ethical and social standards along a company's supply chain. It involves implementing policies and controls to ensure that suppliers and partner companies comply with applicable regulations and standards, such as environmental regulations, worker rights, or product safety.
Sanctions and export control management
… as a subfield of compliance deals with compliance with international sanctions and export control regulations. Companies must ensure that they do not do business with sanctioned countries, organizations or individuals and that their exports are subject to certain restrictions in order to avoid security risks, legal consequences and reputational damage.
Concept of Compliance
Legal & Regulatory compliance
Legal and regulatory compliance covers data privacy, anti-money laundering, anti-corruption laws, and sanctions management to ensure lawful operation of your organization.
Corporate compliance
Corporate compliance encompasses internal policies, integrity measures against corruption and conflicts of interest, and effective governance structures to ensure transparency and financial accountability.

Ethical compliance
Ethical compliance refers to the adherence to ethical and moral principles aimed at ensuring responsible conduct. This includes a commitment to sustainability and ethical business practices.
Leveraging Data and AI for Comprehensive Compliance
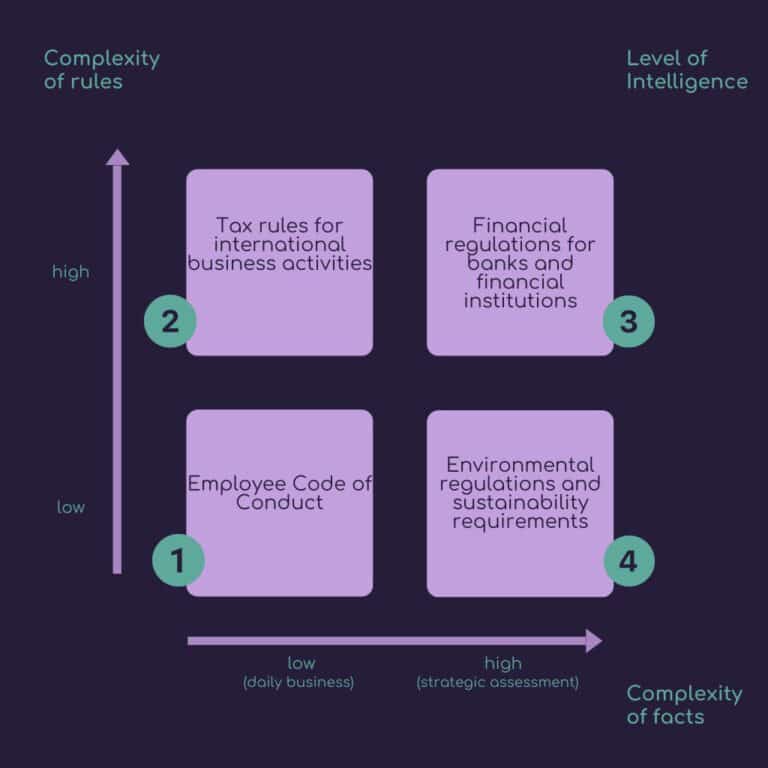
Compliance Challenges
Exemplary fields of action for data-driven compliance

The need for regulation is increasing due to globalization and internationalization, greater consumer awareness and new challenges such as climate protection.

Whereas in the past compliance measures could often be formulated clearly and narrowly, they are becoming increasingly complex and include more and more extensive facts for evaluation and implementation.
Revolutionizing Compliance Through AI
AI driven compliance automation
Unlock the future of compliance with our AI-driven automation, ensuring real-time adaptation to both internal policies and dynamic external regulations. Compliance automation requires
digitized processes and machine-controlled data collection of relevant personal involvement

availability of all relevant dynamically changing regulatory data (e.g. self-imposed internal rules and external regulations)
Handle strategic compliance decisions with support of learning AI technologies
Automate daily business by symbolic AI

Harnessing AI for Enhanced Compliance Efficiency
Why/where do we need AI in compliance processes?

Risk Assessment, pre-vention & prediction:
Analyse of large data volumes to identify potential risks or breaches at an early stage. ML and data mining can be used to identify patterns and outliers. Ex: Evidence of child labor.

Fraud and abuse detection:
AI systems can detect suspicious activity, fraud patterns, or unusual transactions in real time that could indicate compliance violations. Ex: Big data outflow.

Monitoring communi-cations & transactions:
Use of AI to monitor electronic communications and transactions in real time to identify suspicious activity or compliance violations. Ex: spread of fake news in social media.

Dynamic updates of regulations:
Through NLP, compliance policies can be automatically analyzed and translated into action. This can help reduce human error. Ex. automatic update of "rulebooks".

New business models:
By using AI, the scenarios associated with new business models can be simulated and analyzed. Ex: new data-driven business model in the area of data monetization.

former US Deputy Attorney


"If you think that compliance is expensive: try non-compliance.“